
نانومواد|نانو مواد|کاربرد نانومواد
تعریف نانومواد
نانو در زبان یونانی به معنای کوتوله است اما در منابع علمی به عنوان یک مقیاس برای اندازه گیری در سطوح اتمی و مولکولی به کار میرود.
یک نانومتر مساوی است با یک میلیاردم متر یا 10-9 متر.
موادی که یکی از ابعاد آنها در محدوده 1 تا 100 نانومتر باشد را نانو مواد میگوییم. این تعریف بر اساس اندازه بود؛ تعریف دیگری وجود دارد که براساس تأثیر اندازه مطرح میشود. طبق این تعریف، هرگاه با کاهش اندازه ذره خاصیتی جدید در آن مشاهده شود، آن ذره را جزئی از نانو مواد در نظر میگیریم.
در اکثر مواد هنگامی که تا مقیاس نانومتری کوچک میشوند خواص فیزیکی، مکانیکی و حتی ترمودینامیکی در آنها متفاوت میشود. این موضوع باعث شده تا نانومواد پنجرهای جدید به روی کاربردهای پیشرفته و نوین باشد. نانو الیاف، نانو کپسولها، نانو بلورها، نانو کامپوزیتها و نانو پوششها از این دسته مواد هستند که با بکارگیری ساختارهایی در مقیاس نانو خواج جدیدی را از خود ارائه دادهاند.
طبقه بندی نانومواد
نانومواد را با معیارهای متفاوتی میتوان طبقه بندی کرد؛ اما مهمترین معیار طبقه بندی بر اساس ابعاد میباشد. منظور از ابعاد، ابعادی میباشد که در واکنشهای سطحی شرکت داشته باشد. بر این اساس نانو مواد به چهار دسته صفر بعدی (0D)، یک بعدی (1D)، دو بعدی (2D) و سه بعدی (3D) دسته بندی میشوند.
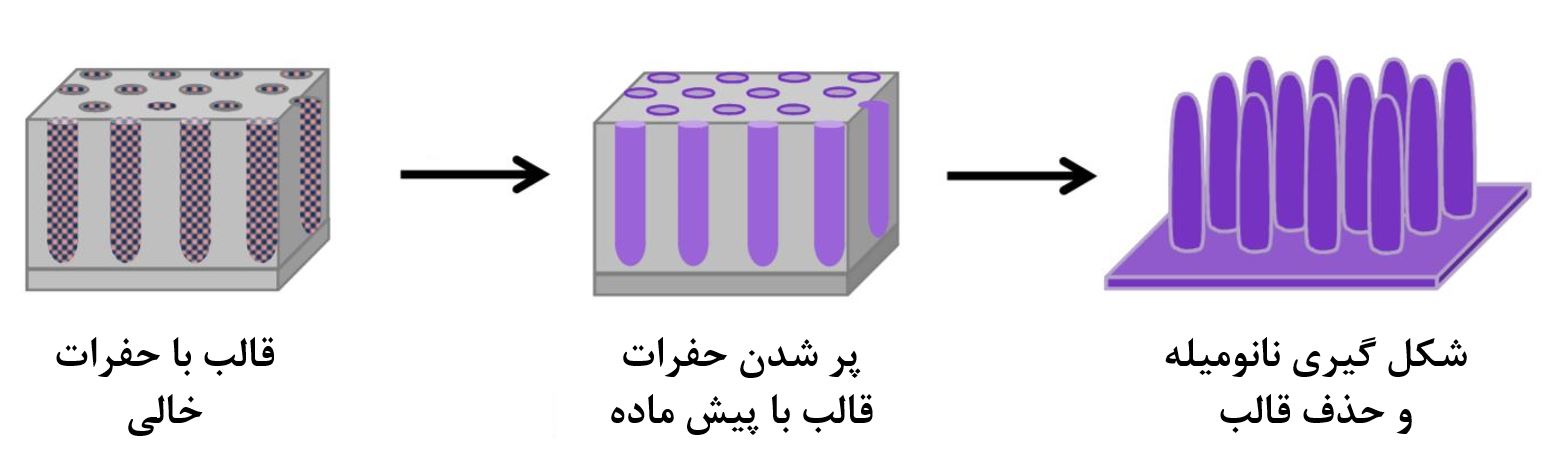
فرآیندهای سنتز نانو
در اکثر مقالات علمی به جای واژه ساخت از اصطلاح سنتز استفاده میشود. به طور جزئی فرآیندهای سنتز نانو مواد به سه گروه تقسیم میشوند که عبارتند از : سنتز شیمیایی نانو مواد، سنتز نانو مواد در حالت جامد و سنتز مواد از فاز بخار.
اکثر خواص شگفت انگیزی که در نانو مواد دیده میشوند به دلیل افزایش نسبت سطح به حجم در آنهاست چون با کوچک شدن مواد تا مقیاس نانو مساحت بسیار زیادی از آنها در معرض واکنشهای شیمیایی قرار میگیرد. به طور کلی خواص مواد نانو مربوط به جنس و اندازه آنها میباشد. به علت خواص گوناگون و شگفت انگیز، نانو مواد در صنایع مختلف کاربردهای بسیار زیادی دارند.
برخی از خواص نانومواد : خواص کاتالیستی، خواص مغناطیسی، خواص فوتوکاتالیستی، خواص نوری، خواص آنتی باکتریال

کاربردهای نانو مواد
کاربردهای نانو مواد بر هیچکس پوشیده نیست و واضح است که لحظه به لحظه کاربرد جدیدی برای نانو مواد در عرصههای متفاوت یافت میشود. این کاربردها دیگر محدود به مهندسی مواد یا علم شیمی و فیزیک نمیباشد بلکه دیگر علوم مثل مکانیک و هوافضا را نیز شامل میشود.
از کاربردهای مهم نانو میتوان در محیط زیست، داروساازی، پزشکی، تولید کامپوزیت، مواد اپتیکی، پوششها، سوختهای نوین، باتریها و مواد شیمیایی اشاره کرد.
کاربرد نانو در مواد شیمیایی به صورت مشارکت در ساخت انواع محلولهای شیمیایی و رنگها میباشد. ساخت رنگهایی با وزن کم نیز در حوزه کاربردهای شیمیایی نانو مواد جای میگیرد. برای مثال از نانو ذراتدوده برای جلوه سیاه رنگ ماشینها استفاده میشود یا زئولیتهای نانو متخلخل برای رها سازی آرام و رسانش مؤثر در کودهای شیمیایی، داروها و عناصر غذایی کاربرد دارند.
برای مثال از مواد نانو میتوان به (USA) Nano-SiO2 آب دوست، (USA) Nano-SiO2 آب گریز،(Porous) Nano-SiO2 متخلخل، نانو سیلیس کلوئید در آب Nano-SiO2 , liquid in water , 25%،(Germany) Nano-SiO2 آّب دوست،
Nano-TiO2 anatase ، Nano-TiO2 Rutile،Nano-TiO2 (Anatase/Rutile)،P25-Degussa Nano-TiO2 ،
Nano-Fe، Nano-Fe2O3-alpha، Nano-Fe3O4، Nano-Al2O3 gamma ، Nano-Al2O3 alpha ، Nano-ZnO، Nano-CuO، MWCNTS، MWCNT-COOH ، MWCNT-OH، MWCNT-NH2 ، SWCNTS ،
SWCNT-COOH ، SWCNT-OH، SWCNT-NH2،Nano-Ag(powder)، Nano-Ag (liquid) 500 ppm ، Nano-Ag (liquid) 1000 ppm ، Nano-Ag (liquid) 2000 ppm ، Nano-Ag (liquid) 4000 ppm ،
Nano-Au، Nano-Au (liquid) ، NanoClay(Montmorillonite) ، NanoClay (Bentonite)، Nano-MgO ، Nano-SiC ، Nano-CaCO3 ، Nano-Co2O3 اشاره کرد.
Nano-materials
Nano means dwarf in Greek, but in scientific sources it is used as a scale for measuring at the atomic and molecular levels. One nanometer is equal to one billionth of a meter or 10-9 meters.
Materials whose one of the dimensions is in the range of 1 to 100 nanometers are called nanomaterials. This definition was based on size; There is another definition based on the effect of size. According to this definition, whenever a new property is observed in a particle by reducing its size, we consider that particle as a part of nanomaterials.
In most materials, their physical, mechanical, and even thermodynamic properties vary as they shrink to the nanometer scale. This has led to new window nanomaterials for advanced and modern applications. Nanofibers, nanocapsules, nanocrystals, nanocomposites and nanocoatings are among these materials that have introduced new structures using nanoscale structures.
Nanomaterials can be classified by different criteria; But the most important criterion is classification based on dimensions. Dimensions are dimensions that participate in surface reactions. Based on this, nanomaterials are classified into four categories: zero-dimensional (0D), one-dimensional (1D), two-dimensional (2D) and three-dimensional (3D).
In most scientific articles, the term synthesis is used instead of the word construction. In particular, the processes of nanomaterial synthesis are divided into three groups, which are: chemical synthesis of nanomaterials, synthesis of nanomaterials in solid state and synthesis of materials from vapor phase.
Most of the amazing properties seen in nanomaterials are due to the increase in surface-to-volume ratio because as materials shrink to nanoscale, a large area of them is exposed to chemical reactions. In general, the properties of nanomaterials are related to their material and size. Due to their various and amazing properties, nanomaterials have many applications in various industries.
Some properties of nanomaterials: catalytic properties, magnetic properties, photocatalytic properties, optical properties, antibacterial properties.
The applications of nanomaterials are not hidden from anyone and it is clear that new applications for nanomaterials are being found in different fields moment by moment. These applications are no longer limited to materials engineering or chemistry and physics, but also other sciences such as mechanics and aerospace. Important applications of nano can be found in the environment, pharmacy, medicine, composite manufacturing, optical materials, coatings, new fuels, batteries and chemicals.
The application of nano in chemicals is in the form of participation in the manufacture of various chemical solutions and dyes. The manufacture of lightweight paints is also in the field of chemical applications of nanomaterials. For example, nanoparticles are used to make cars black, or nanoporous zeolites are used for smooth release and effective conductivity in chemical fertilizers, drugs, and nutrients.
Examples of nanomaterials are hydrophilic Nano-SiO2, hydrophobic Nano-SiO2, porous Nano-SiO2, Nano-SiO2 nano-SiO2, liquid in water, 25%, ( Germany) Nano-SiO2 water friend,
Nano-TiO2 anatase, Nano-TiO2 Rutile, Nano-TiO2 (Anatase / Rutile), P25-Degussa Nano-TiO2,
Nano-Fe, Nano-Fe2O3-alpha, Nano-Fe3O4, Nano-Al2O3 gamma, Nano-Al2O3 alpha, Nano-ZnO, Nano-CuO, MWCNTS, MWCNT-COOH, MWCNT-OH, MWCNT-NH2, SWCNTS,
SWCNT-COOH, SWCNT-OH, SWCNT-NH2, Nano-Ag (powder), Nano-Ag (liquid) 500 ppm, Nano-Ag (liquid) 1000 ppm, Nano-Ag (liquid) 2000 ppm, Nano-Ag ( liquid) 4000 ppm,
Nano-Au, Nano-Au (liquid), NanoClay (Montmorillonite), NanoClay (Bentonite), Nano-MgO, Nano-SiC, Nano-CaCO3, Nano-Co2O3 mentioned.
درباره ما
شركت مينا تجهيز آريا با سالها تجربه و با استفاده از تخصص،تعهد، تجربه و دانش هاي نوين اقدام به تهيه، توزيع مواد شیمیایی ( آزمایشگاهی ، صنعتی ) و تجهيز لوازم آزمايشگاهي، شيشه آلات و كليه ملزومات آزمايشگاهي از شركت هاي داخل و خارج كشور نموده است.
برای پرسش و پاسخ و دریافت قیمت و موجودی با کلیک روی لینک زیر به تلگرام شرکت پیام دهید
آدرس : تهران - میدان توحید- خیابان امیر لو(نبش کوچه خودرو) - پلاک 42- طبقه دوم - واحد5
ایمیل : minatajhiz_aria@yahoo.com
شماره ها تماس : 02166901187 - 02166900058
شماره های همراه :09362048289 - 09927282910
شماره های واتس آپ ، ایتا ، تلگرام و روبیکا : 09927282910

